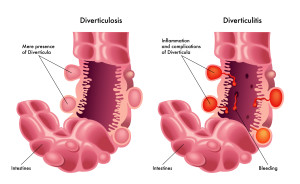
 Diverticulitis is a condition of the bowels that occurs when diverticula, small pouches, form along the colon and become infected. Diverticula are harmless and are commonly formed in the body after the age of 40. About half of the population over the age of 60 have diverticula in their colon. Individuals are usually unaware of them unless they are spotted during a colonoscopy or a barium enema x-ray. Diverticula form in the digestive system, which is refered to as having Diverticulosis, but are most commonly found in the large intestine on the lower left side of the body.
Diverticulitis is a condition of the bowels that occurs when diverticula, small pouches, form along the colon and become infected. Diverticula are harmless and are commonly formed in the body after the age of 40. About half of the population over the age of 60 have diverticula in their colon. Individuals are usually unaware of them unless they are spotted during a colonoscopy or a barium enema x-ray. Diverticula form in the digestive system, which is refered to as having Diverticulosis, but are most commonly found in the large intestine on the lower left side of the body.
Diverticula can become infected, which is the cause of diverticulitis. This infection can lead to extreme pain and difficulty in bowel functions. Mild flare ups of diverticulitis can be treated with pain medication, rest and dietary modifications. If the infection becomes severe and causes acute pain, surgery may be the only option.
Complications of diverticulitis can occur in individuals with the disease. In some instances, the bowel can become constricted, creating a blockage. Fistulas can form, which perforate the bowel and can create “holes” in adjacent organs such as the bladder. Peritonitis is also a possibility, when an infected diverticula bursts and waste is released into the body cavity. This happens in rare, but very serious, cases of diverticulitis and can be life threatening. Emergency surgery is required in such instances.
A colectomy is a surgical procedure which involves removing the diseased section of the colon. New technology such as the robot-assisted da Vinci® machine has made this surgery as minimally invasive as possible for thousands of patients suffering from diverticulitis. Removing part or all of the colon is only done in severe cases.
Symptoms of Diverticulitis:
- Pain, normally on the lower left side of the abdomen, for several days
- Fever
- Nausea or vomiting
- Constipation
Who can get Diverticulitis?
- Men and women are equally affected by this disease
- Individuals over the age of 40 are susceptible to diverticula, which increases the chance of developing diverticulitis
What can I do to avoid the disease?
- Maintain a healthy, fiber rich diet. Fibrous foods such as fruits and vegetables help to soften the waste moving through the colon. This reduces the pressure on the intestines.
- Daily exercise
- Do not smoke. Individuals who smoke are more likely to form diverticula than those that don’t smoke tobacco.
- Drink plenty of fluids to help move waste through the colon.
If you feel like you have symptoms of diverticulitis, please contact a physician immediately to be evaluated and treated. Search for a Colon/Rectal surgeon at www.ipalc.org
Share on Facebook



 Southwest Florida Medicine.com is dedicated to bringing you the very best health information available today!
Subscribe or check back regularly!
Southwest Florida Medicine.com is dedicated to bringing you the very best health information available today!
Subscribe or check back regularly!